Nova Outburst Offers Rare Skywatching Opportunity
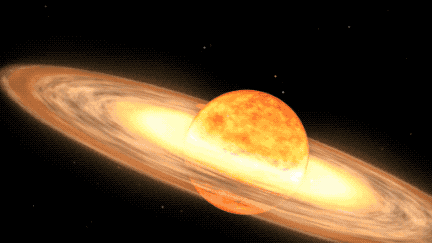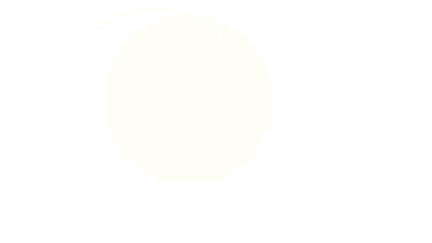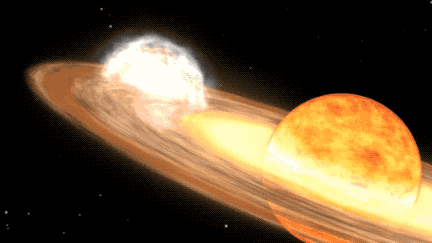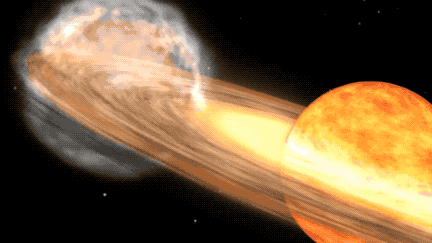
A spectacular nova outburst that will be visible to the naked eye is anticipated to grace the night sky this year, presenting a unique celestial event for skywatchers. The celestial phenomenon is set to be showcased by a star system named T Coronae Borealis (T CrB), situated approximately 3,000 light-years away from our planet. T CrB comprises a red giant star and a white dwarf that revolve around each other.
The Phenomenon of a Nova Outburst
During the process where the white dwarf appropriates enough material from its red giant companion, a brief burst of nuclear fusion is ignited on the white dwarf’s surface, leading to what is identified as a nova outburst. This forthcoming outburst is expected to illuminate the constellation Corona Borealis, commonly referred to as the Northern Crown, which encompasses a semicircle of stars. The outburst is projected to take place from February to September 2024 and is anticipated to shine as brightly as the North Star in our night sky for a fleeting period before gradually fading away, as indicated by NASA officials in a statement.
A Rare Occurrence
This upcoming nova outburst presents a relatively rare skywatching opportunity, as these events only happen approximately once every 80 years, according to NASA. This recurrent nova, which was last observed to explode in 1946, is among the mere five such phenomena recorded within the Milky Way galaxy. To witness the outburst, observers are advised to direct their vision towards Corona Borealis, situated between the constellations Boötes and Hercules, where the outburst will manifest as a luminous “new” star in the nocturnal firmament.
Significant Brightness Increase
Ordinarily, these binary stars exhibit a magnitude of +10, which is too faint to be discerned with the naked eye. However, during the outburst, the stellar system will shine at a magnitude of +2, comparable to the brightness of the North Star, Polaris. Subsequently, following the peak brightness, the nova should remain visible to the unaided eye for several days and up to a week with the assistance of binoculars before gradually diminishing – a phenomenon that may not occur again for another 80 years, as per NASA officials.
The Intriguing Process Behind the Nova Outburst
The explosive duo of stars consists of a white dwarf, a compact and dense stellar remnant, in conjunction with a larger red giant star in the advanced stages of stellar evolution, characterized by an inflated and diffuse outer atmosphere. The proximity of these gravitationally-bound stars results in the red giant expelling its outer layers onto the white dwarf as it becomes unstable due to heightened temperature and pressure. The accumulation of material elevates the temperature of the white dwarf’s dense atmosphere, inciting a thermonuclear reaction that manifests as the nova observed from Earth. Following this display, the process will recur as the white dwarf accumulates sufficient material to spark another outburst.
Image/Photo credit: source url